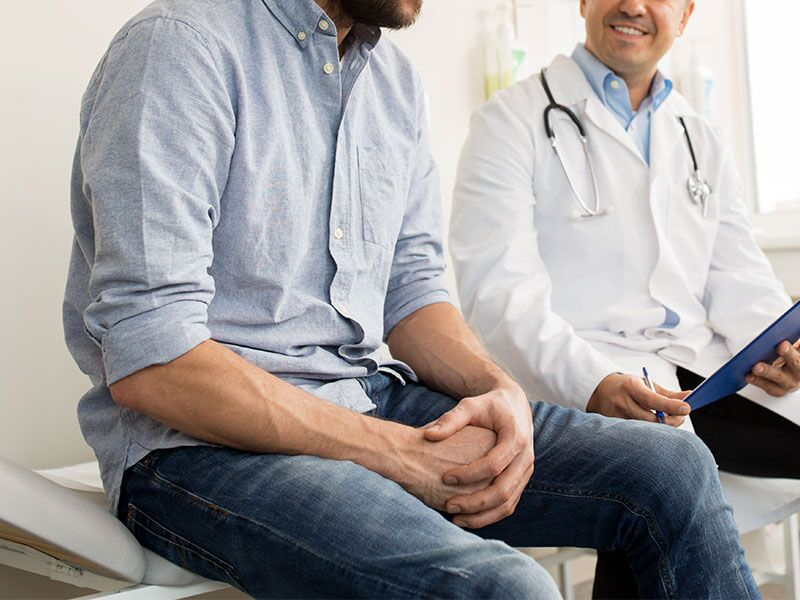
Passive assisted stretching is a dynamic and collaborative method that leverages the support of a partner to enhance flexibility. This approach involves a series of stretches where the individual being stretched remains passive while a partner provides external assistance. Understanding the key components of passive assisted stretching is crucial for maximizing its benefits and ensuring a safe and effective stretching experience.
Partner involvement:
The core element of passive assisted stretching is the involvement of a partner. This partner can be a professional trainer, a fitness buddy, or even a friend. The partner actively assists in guiding the stretches, providing support, and ensuring proper alignment. The collaborative nature of this stretching technique sets it apart from independent stretching methods.
Passive participant:
The individual being stretched in passive assisted stretching remains passive throughout the process. Unlike active stretching where the individual engages muscles to create the stretch, passive participants focus on relaxation and yielding to the stretch. This allows for a deeper release of tension and optimal elongation of muscles.
Controlled pressure:
The partner in passive assisted stretching applies controlled pressure to facilitate gradual assistance in stretching. This controlled approach ensures that the stretch remains within a safe and comfortable range for the individual being stretched. It allows the muscles to adapt to the stretch without causing undue stress or strain.
Variety of stretches:
Passive assisted stretching encompasses a variety of stretches, each targeting different muscle groups. These stretches can be tailored to the individual’s specific flexibility goals or areas of focus. The variety ensures a comprehensive and well-rounded approach to flexibility training.
Breath awareness:
Breath awareness is often emphasized in passive assisted stretching. Deep, rhythmic breathing helps enhance relaxation, reduces tension, and promotes mindfulness during the stretching session. Focusing on breath contributes to a more enjoyable and meditative experience.
Cool down:
A passive assisted stretching session typically concludes with a cool-down period. This involves incorporating gentle movements to gradually bring the body back to a state of rest. The cool-down helps prevent post-stretching soreness and promotes a smooth transition from the stretching session.
Passive assisted stretching involves partner collaboration, a passive participant focusing on relaxation, a gentle warm-up, supportive props, controlled pressure for gradual assistance, a variety of stretches targeting different muscle groups, breath awareness, and a concluding cool-down.